Probably you agree with us if we say that when choosing a floating pontoon, location is the king, and as the king, location also determines whether it is possible or financially worthwhile to install a pontoon in the specific location.
How do you assess the suitability of the location and how to make decisions?
It’s not so complicated as you might think. In the following sections, we will show you what we look at when we consider our natural conditions, so that you could also be able to make an initial assessment independently.
Location of the floating pontoon: important factors
To save your time, let’s just say where you can not install a pontoon: floating pontoons can not be placed on open beaches or on the coast; suitable locations are either naturally well-protected beaches or a port basin protected by a breakwater.
1. Ice conditions
Fortunately, it is possible to estimate ice conditions in other seasons than only in winter. How?
You only have to become a keen observer and study the water body on the basis of the following knowledge:
- in bays that are closed and protected from wind, ice melts without moving or moves only slightly under the influence of winds;
- if large trees are not growing very close to the shore, it is quite likely that ridged ice reaches there;
- The ice conditions are also visible from the rocks: if they have been shifted, ridged ice has occurred.
If ridged ice occurs then it is highly probable that a boat pontoon can not be installed, as the ice would destroy it every winter. If no other location is possible, you can consider removing the floating pontoon for the winter and re-installing it in the spring, but here you have to take into account the financial and temporal cost of this activity.
2. Openness of the beach to wind
In the case of inland water bodies, there is generally no need to worry about wind, but when planning a pontoon into the sea, you should be very careful at this point.
You can check the dominating wind direction of your beach using a wind rose. It is convenient to use the Global Wind Atlas map on their website. Just click on the desired location, select “Wind Rose” from the right and you will see the winds that are dominant in this area:
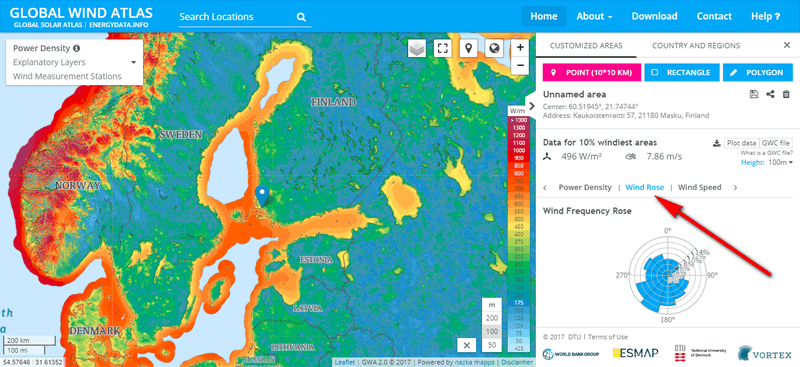
Image: a screenshot from the Global Wind Atlas website
This way you can identify the most dangerous wind direction, after which you have to check from the map and in the location itself, whether there is a free rain for the winds to blow from that direction, or if there is something that provides protection, such as a cape, peninsula or island, which makes the waves safe in the chosen place.
3. Wave height
Weather conditions on the sea and on inland water bodies (lake, river, pond) are very different. The largest difference between the open sea and inland water bodies is wave height – inland, winds are slowed by forests and other vegetation, but on the sea where there are no obstacles, the wind has the ability to collect speed, and thus, there are significantly higher waves on open sea than for example on a lake.
So, first of all, get a clear idea of the average wave height at the future location of the boat pontoon and also check the maximum wave height numbers to know what kind of forces your pontoon has to withstand.
4. Average water level
The water level in the sea and in inland waterways changes according to seasons and winds, for example, in extreme cases the level of the Baltic Sea has been 2.5 meters over and 1.2 meters below the mean.
On inland water bodies, water level depends on precipitation and snow melt. Fluctuations are greatest in the springs after snow-rich winters and in rainy periods.
Due to the constant fluctuation of the water level, it is important that you take the average water level at the desired location into account when choosing a pontoon. How do you find out that?
The average water level is generally visible on the beach and visual inspection is sufficient. If it is an unknown place, we also recommend talking to the older people in the area, who have lived there for a long time and can provide information about a longer time period.
5. Water depth from the coastline
If the location is by the sea, you can also get help from sea maps that have depths indicated on them (for example, Navionics’ map that is to a large extent freely available).
How does knowledge of water depth help you in your planning process?
If you know the proper water depth from the average coastline, you also have a clear picture of where you can keep your boat and jump into the water head first without worrying, and most importantly – you can calculate how long of a floating pontoon you need.
For example, if the coastline is too low and water that is of a sufficient depth for mooring is far, it means that it is necessary to build a very long pontoon, which makes the whole project impractical, as the costs get out of control.
In conclusion
Let us revise the important things again.
Floating pontoons can be installed in a water area limited by a pier or on a naturally well-protected beach. On an open beach or coast, the pontoon does not withstand the forces of nature.
Five factors need to be assessed at the location:
- ice conditions;
- openness of the coast to the wind;
- wave height;
- average water level;
- water depth from the shoreline.
If you have any questions about what you read or would like to discuss the installation of the floating pontoon, please contact our expert at the bottom of the page.






